Restriction Endonucleases
Choose Type:
- Digestion of Agarose-Embedded DNA
- Standard Digest Using RE-Mix®
- Double Digest Protocol using Two RE-Mix® Enzymes
- Optimizing Restriction Endonuclease Reactions
- Double Digest Protocol using One RE-Mix and One Standard Restriction Enzyme
- Protocol for Direct Digestion of gDNA during droplet digital PCR (ddPCR)
- Double Digest Protocol with Standard Restriction Enzymes
-
Restriction Endonucleases: Molecular Cloning and Beyond
-
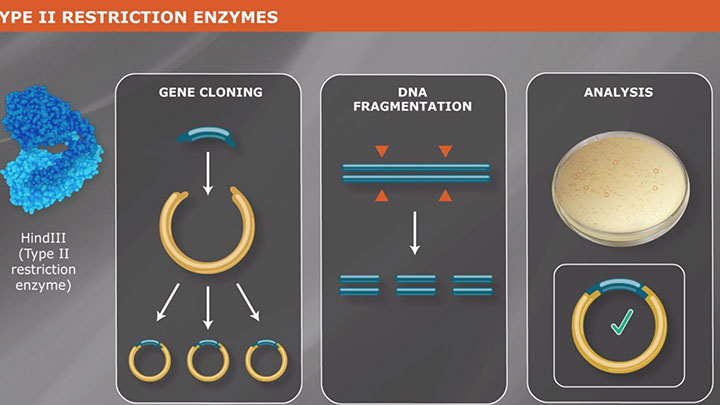
Type II Restriction Enzymes: What You Need to Know | NEB
Read about Type II restriction enzymes and the distinguishing properties of the four principle subtypes.
-
A Modern Day Gene Genie Sir Richard Roberts on Rebase
-
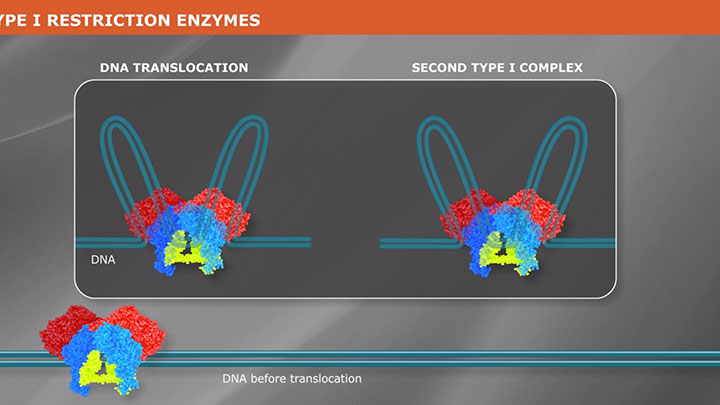
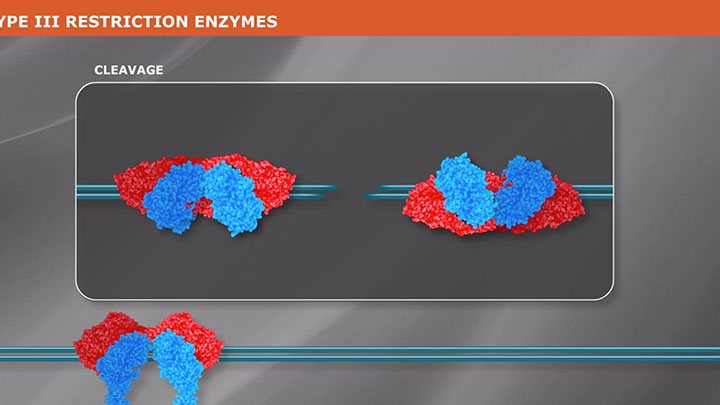
Restriction Enzyme Cleavage: ‘single-site’ enzymes and ‘multi-site’ enzymes
Restriction enzymes are proteins used to fragment and clone DNA, but their biological function is to protect bacteria and archaea against viral infections.
-
Whole genome assembly from next generation sequencing data using restriction and nicking enzymes in optical mapping and proximity-based ligation strategies
High throughput sequencing methods have revolutionized genomic analysis by producing millions of sequence reads from an organism’s DNA at an ever decreasing cost.
- NEB Restriction Enzyme Activity Poster
- DNA Sequences and Maps Tool
- REBASE®
- Alphabetized List of Recognition Sequences
- Cleavage Of Supercoiled DNA
- Compatible Cohesive Ends and Generation of New Restriction Sites
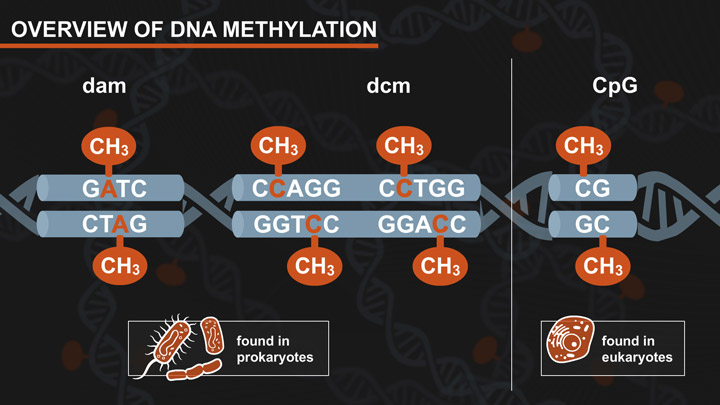
- Dam-Dcm and CpG Methylation
- Enzymes with Multiple Recognition Sequences
- Enzymes with Nonpalindromic Sequences
- Frequencies of Restriction Sites
- Interrupted Palindromes
- Isoelectric Points (pI) for Restriction Enzymes
- Isoschizomers
- Recleavable Blunt Ends
- Recleavable Filled-in 5' Overhangs
- Time-Saver™ Qualified Enzymes
- Type IIS Restriction Enzymes
- Why Choose Recombinant Enzymes?
- Restriction Enzyme Troubleshooting Guide
- Activity at 37°C for Restriction Enzymes with Alternate Incubation Temperatures
- Activity of Restriction Enzymes in PCR Buffers
- Alteration of Apparent Recognition Specificities Using Methylases
- Cleavage Close to the End of DNA Fragments
- Dam and Dcm Methylases of E. coli
- Digestion of Agarose-Embedded DNA: Info for Specific Enzymes
- Double Digests
- Effects of CpG Methylation on Restriction Enzyme Cleavage
- Heat Inactivation
- NEBuffer Activity/Performance Chart with Restriction Enzymes
- Optimizing Restriction Endonuclease Reactions
- Restriction Endonucleases - Survival in a Reaction
- Restriction Enzyme Diluent Buffer Compatibility
- Restriction Enzyme Tips
- Restriction Enzymes for Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR)
- Restriction Enzymes requiring multi-sites for efficient cleavage
- Restriction of Foreign DNA by E. coli K-12
- Site Preferences
- Star Activity
- Traditional Cloning Quick Guide
- Crystal Structure of the 8 bp-Specific Restriction Enzyme SwaI (2015)
Feature Articles
Brochures
Web Tools
Selection Tools
Troubleshooting Guides
Usage Guidelines
Posters
- Shah, S., Sanchez, J., Stewart, A., et al. (2015) Probing the Run-On Oligomer of Activated SgrAI Bound to DNA PLoS One; 10(4), PubMedID: 25880668, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124783.
- Fomenkov, A., Lunnen, K.D., Zhu, Z., Anton, B.P., Wilson, G.G., Vincze, T. and Roberts, R.J. (2015) Complete genome sequence and methylome analysis of bacillus strain x1 Genome Announc; 3(1), PubMedID: 25700417
- Roberts, R.J., Vincze, T., Posfai, J., Macelis, D. (2015) REBASE - A database for DNA restriction and modification: enzymes, genes and genomes Nucleic Acids Res; 43, D298-D299. PubMedID: 25378308
- Kamps-Hughes, N., Quimby, A., Zhu, Z., Johnson, E.A. (2013) Massively parallel characterization of restriction endonucleases Nucleic Acids Res ; 41(11), e119. PubMedID: 23605040, DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt257
- Morgan, R.D., Luyten, Y.A., Johnson, S.A., Clough, E.M., Clark, T.A. and Roberts, R.J. (2016) Novel m4C modification in type I restriction-modification systems. Nucleic Acids Res; Nov, 2;44(19):9413-9425. PubMedID: 27580720
- Fu YB, Peterson G. W., Dong Y (2016) Increasing Genome Sampling and Improving SNP Genotyping for Genotyping-by-Sequencing with New Combinations of Restriction Enzymes G3 (Bethesda); 6:4, 845-846. PubMedID: 26818077
- Blow, M.J., Clark, T.A., Daum, C.G., Deutschbauer, A.M., Fomenkov, A., Fries, R., Froula, J., Kang, D.D., Malmstrom, R.R., Morgan, R.D., Posfai, J., Singh, K., Visel, A., Wetmore, K., Zhao, Z., Rubin, E.M., Korlach, J., Pennacchio, L.A. and Roberts, R.J. (2016) The Epigenomic Landscape of Prokaryotes. PLoS Genet; Feb 12;12(2):e1005854, PubMedID: 26870957, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005854
- Callahan, S.J., Luyten, Y.A., Gupta, Y.K., Wilson, G.G., Roberts, R.J., Morgan, R.D. and Aggarwal, A.K. (2016) Structure of Type IIL Restriction-Modification Enzyme MmeI in Complex with DNA Has Implications for Engineering New Specificities. PLoS Biol; Apr 15;14(4):e1002442, PubMedID: 27082731
- Roberts, R.J., Vincze, T., Posfai, J., Macelis, D. (2014) REBASE - A database for DNA restriction and modification: enzymes, genes and genomes Nucleic Acids Res;
- Loenen, W.A., Raleigh, E.A. (2014) The other face of restriction: modification-dependent enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res; 42, 56-69. PubMedID: 23990325
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.